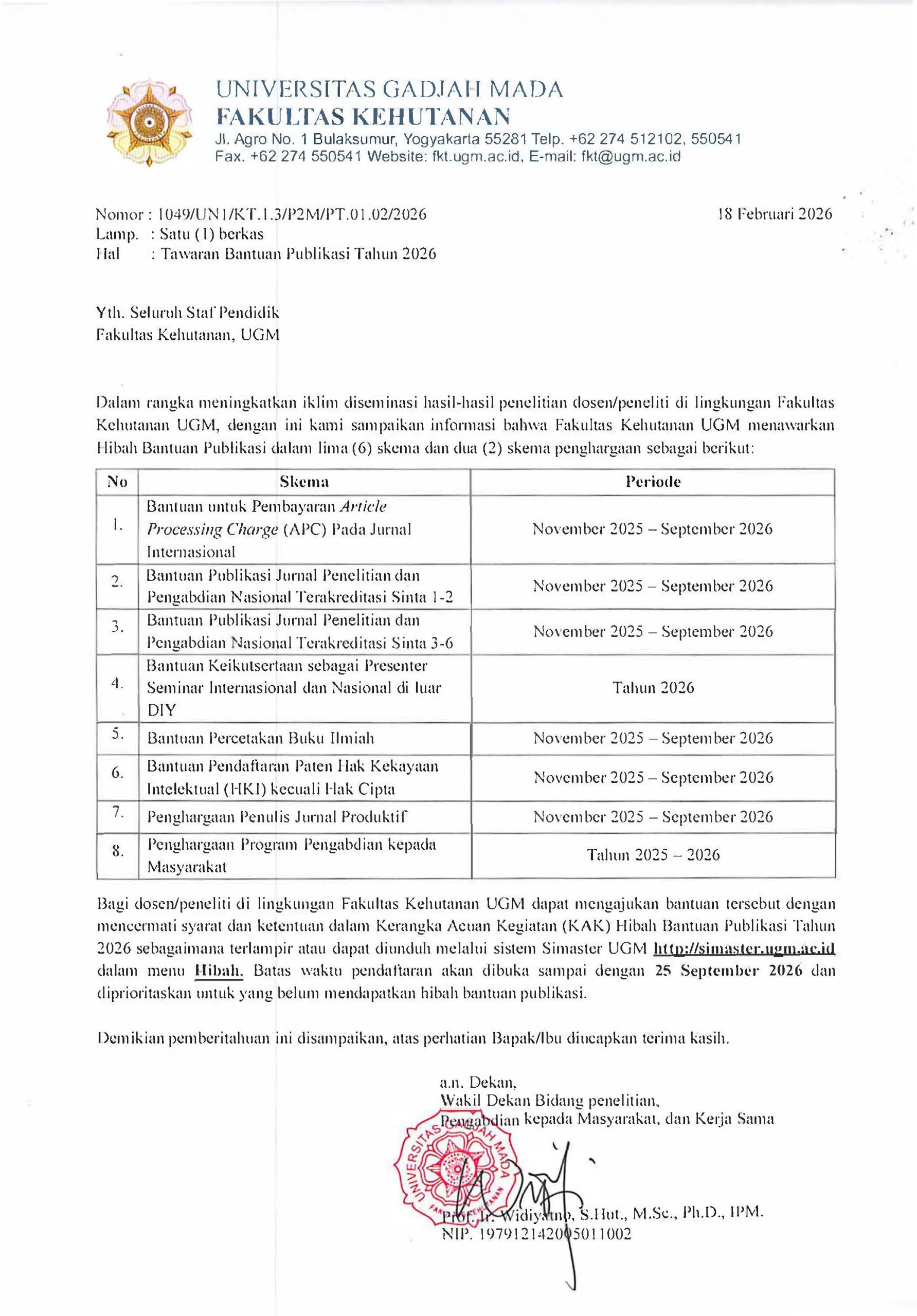
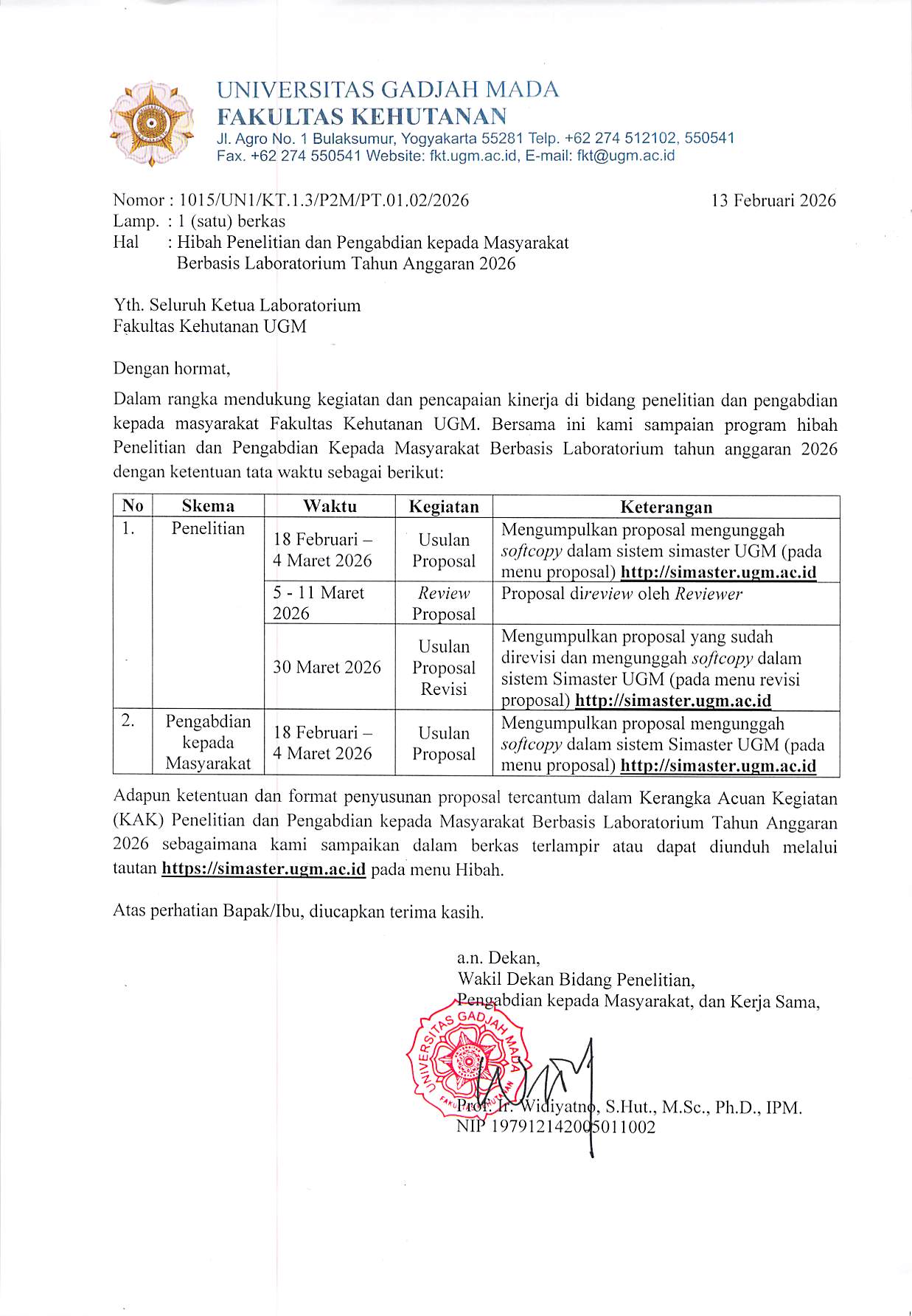
Abstract
Santalum album Linn. (sandalwood) is a commercially important species due to the essential oils derived from its heartwood. This species has been currently threatened by overharvesting and habitat fragmentation. Therefore, this study aims to assess genetic diversity and population structure of seven Indonesian sandalwood populations using eight nuclear simple sequence repeat (nSSR) markers. The samples comprised 202 individuals from one ex-situ conservation